Home |
Key Elements |
VMware vSphere Key Elements:
- Computing and memory resources: hosts, clusters, and resource pools
- Storage resources: datastores and datastore clusters
- Networking resources: networks
- Virtual machines
Hosts, clusters, and resource pools provide flexible and dynamic ways to organize the aggregated computing and memory resources in the virtual environment and link them back to the underlying physical resources.
When two or more physical machines are grouped to work and be managed as a whole, the aggregate
computing and memory resources form a cluster.
In VMware vSphere, clusters are used for high availability and to balance computing capability (via DRS):
- HA: If a physical host (running Virtual Machines) goes down, one of the other physical hosts start up the virtual machines that the original host was running
- DRS: If a physical host is over-utilized by a virtual machine, that virtual machine is dynamically moved to another physical host in the cluster
 |
Computing and memory resources from hosts and clusters can be finely partitioned into a hierarchy
of resource pools. A resource pool is used to ensure that CPU and RAM resources are allocated fairly (or based on pre-defined policies)
across systems. The CPU and RAM resources in the pool are allocated based on the CPU and RAM shares that are defined.
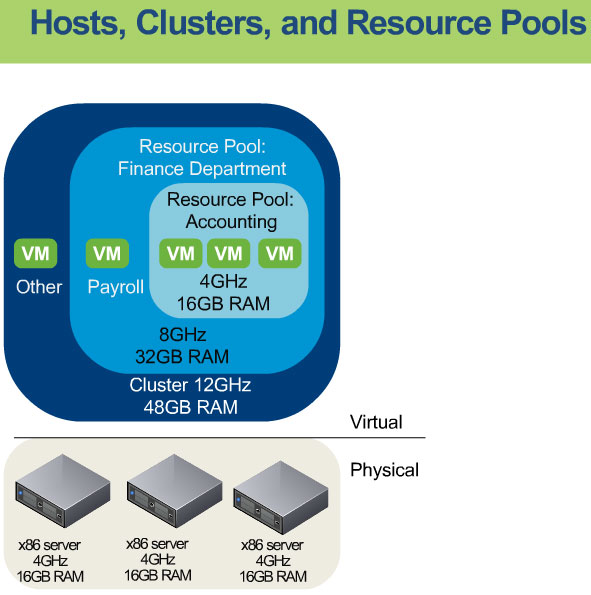 |
Resource pools can be contained inside clusters. Clusters contain hosts or resource pools, and Datacenters contain Hosts and Clusters.
To setup a resource pool the limit, reservation, and share settings for both CPU & Memory for all virtual guest machines in the pool must be configured.
Also alarms (alerts) and permissions on both clusters and resources pools can be configured.
Note: Resources are shared on a resource pool level, not on a per VM level. Resource pool can be created on individual hosts, only if hosts are not clustered.
The following information is used to create resource pools:
- Name: Name of the resource pool
- Shares: Number of shares to be allocated to every VM
- Reservation: Minimum resources guaranteed to VM’s
- Expandable reservation: There are two options YES/NO, if say YES, if reservation of existing resource pools are not available they can be used from Parent resource pool, If select NO, then host won’t be able to power ON the VM.
- Limit: Maximum resources any VM, under this resource pool would get.
NB: Update above information for vSphere 5.
Datastores are virtual representations of physical storage resources. These physical storage resources can come from the following sources:
- Local SCSI, SAS, or SATA disks of the server
- Fibre Channel SAN disk arrays
- iSCSI SAN disk arrays
- Network Attached Storage (NAS) arrays
A datastore cluster is an aggregation of multiple datastores into a single logical, load-balanced pool.
Networks in the virtual environment connect virtual machines to one another and to the physical network
outside of the virtual datacenter.
Because a host represents the aggregate resources of a physical x86 server, if the physical server has four dual-core CPUs running at 4GHz each and 32GB of system memory, the host has 32GHz of computing power and 32GB of memory. This available CPU and RAM resources will be shared amongst the running virtual machines that are assigned to the host.
If a cluster contains eight servers with four dual-core CPUs each running at 4GHz and 32GB of memory, the cluster has an aggregate 256GHz of computing power and 256GB of memory available for running virtual machines.
Resource pools are partitions of computing and memory resources from a single host or a cluster. Resource pools can be hierarchical and nested.
http://www.yellow-bricks.com/2009/11/13/resource-pools-and-shares/
http://vmzare.wordpress.com/2007/02/27/creating-resource-pools/
http://pubs.vmware.com/vsphere-50/index.jsp
http://vinfrastructure.it/wp-content/uploads/2011/11/VCP5-study-notes-EN-1.1.pdf - Study Notes
http://vcp5.wordpress.com
VTSP5 Boot Camp
Home |
Key Elements |